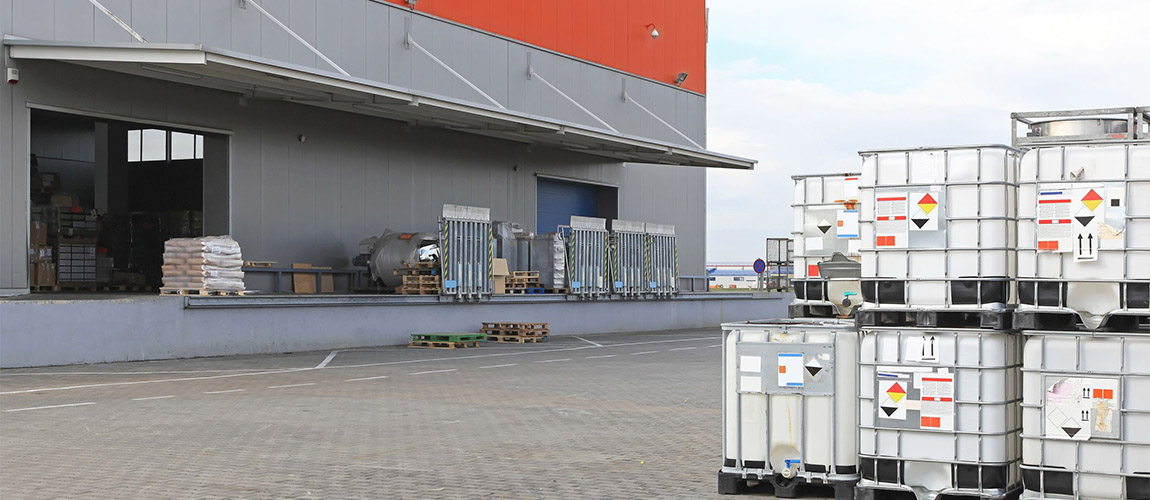
WE PERFORM:
- Short-time storage of goods (with regards on different capacities of continuous transport types on entry and outlet); the goods of different character and properties (bulk material, pieces, palettes, dangerous goods and goods of specific properties, etc.),
- Redistribution (combination) of different goods in order to make single shipments according to the customer's requirements,
- Combination of more small shipments delivering to the different customers,
- Dividing big shipments of the same goods types from different producers into one big shipment for one or several customers,
- Grouping more small shipments from different producers into one big shipment for one or more customers,
- Commission storage,
- Packing and unpacking the palettes,
- Filling and discharging the freight components of the combined transport (big containers, etc.).
WE TRY USING THE STORAGE SYSTEMS:
- Push systém, that is a standard system for goods distribution. In this system the storage accepts the material produced by Manufacturing Corporation to be put on the market as soon as possible. Therefore it is expected that material coming from the warehouse will be removed as soon as possible. In the case that the material is producing faster than selling the products are collected in such warehouse. So storage in push system is intended for absorbing abnormal production of Manufacturing Corporation. Production “pushes” the products into the warehouse without any respect to the real requirements of consumer.
- Pull system is an opposite of the push system. In the case of pull system it is not required creating any stocks, resp. only minimum stocks. The producer makes only such amount of products necessary for the final consumer. So the customer “pulls” the products from the producer. Instead of absorbing the abnormal stocks, the warehouses are only discharge distribution centres offering higher level of the customer service because they offer supplementary services and also moves the storage further to the customers.
- Cross-Dock is a system based on the principle of immediate transferring the goods. Warehouse is not use primary for goods storage but it is only distribution, or mixing centre. Goods is usually transported into the warehouse by mass transport, for example by railway transport, (where at longer transport distances the transport costs are lower); goods is immediately divided and combined in necessary amount with the other products into a single shipment according to the customer's requirements. This arranged shipment is consequently distributed by less capacity transport type, usually by road transport. In the Cross-Dock system, the products are not principally stored in the warehouse but are further transferred and sent as soon as possible. This system is relatively applied in the logistics centres and used as an inseparable part of the acquisition processes providing material transfer to the production lines, for example in the case of motor vehicle production.
Today the Cross-Dock system is belonged to the standard tools enabling increasing the flow in the warehouse, increasing goods flow and total distribution costs decreasing.
At present the supply range philosophy is changed into the customer range philosophy. It requires from a supplier to be more capable, mainly to be able of expending the goods fast and on time.
Cross-Dock system is suitable for any sort of goods because it is not important goods character but effective transfer organizing and filling the shipments in order to optimize total transport, manipulation and stock costs. The Goods is concentrated on the expedition area in the warehouse and consequently the combined shipments are made for separate transport destinations.